Outcome Review of Modified Central Mound Technique in Breast Reduction AND Mastopexy
- Corresponding Author:
- Omar Alnobani
Plastic Surgery Registrar, Manchester Foundation Trust, United Kingdom
E-mail: omar.alnobani@nhs.net
Received: 12-Apr-2022, Manuscript No. ijocs-22-60401; Editor assigned: 14-Apr-2022, PreQC No. ijocs-22-60401(PQ); Reviewed: 12-May-2022, QC No. ijocs-22-60401(Q); Revised: 15-May-2022, Manuscript No. ijocs-22-60401(R); Published: 20-May-2022, DOI: 10.37532/1753-0431.2022.16(4).240
Abstract
Background: The Central Mound (CM) technique is one of the most reliable and safe mammoplasty techniques, based on the use of a highly
vascular central pedicle.
Method: From January 2020 to December 2020, a retrospective review of 28 patients, who underwent reduction mammoplasty or mastopexy
using our modified technique, were included in this study. All procedures were performed by the senior author of this paper in a private
setting. Patients’ demographics, operative and postoperative outcomes were collected and analyzed.
Results: In this study, 28 patients identified for inclusion. The mean age was 44.5 years, and mean Body Mass Index (BMI) was 30.2 kg/m2.
Postoperatively, mean follow up period was 5.5 months, with no mortalities and few morbidities and high satisfaction rate.
Keywords
Central mound; Reduction mammoplasty; Mastopexy, Outcomes
Introduction
Macromastia, or sometimes known as symptomatic mammary hypertrophy, is a common condition in women. Excessive breast tissue can cause physical problems such as musculoskeletal pain, posture difficulties and erythema intertrigo. Moreover, it can cause psychological distress and negatively impact body image perception and quality of life [1,2].
The mainstay treatment for macromastia is a reduction mammoplasty, which is a highly prevalent aesthetic breast procedure. There are various techniques for reducing mammoplasty, and the type of nipple pedicle employed in breast reconstruction is a matter of debate. There has been considerable development and refinement in the different techniques of reduction mammoplasty, categorized by different pedicle designs and skin pattern reductions [3-9]. One of those commonly used procedures is the Central Mound (CM) mammoplasty, which has proved effective at volume reduction, minimizing scar burden and retaining the neurovascular pedicle and lactational potential [4,10].
In 1981, Balch introduced the CM technique as an unconventional approach, but it has come forth as a safe and effective approach consisting of a wide range of advantages [11]. This technique revolves around opting for a highly vascular glandular pedicle directly from the chest wall, with a specific feature that it can be used reliably in re-reductions regardless of the pedicle design in the prior reduction [3,4].
This study has revisited the central mound technique with touch up modifications to maximize the overall outcome. The aim was to analyze and evaluate the postoperative results using this technique in terms of post operative complications and patient’s satisfaction.
Methods
■ Study design
A retrospective review of all patients who underwent reduction mammoplasty or mastopexy using a modified CM technique got included in this study from January 2020 to December 2020. All procedures were performed by the senior author of this article. Patients’ demographics, comorbidities, operative and postoperative details were collected and statistically analyzed.
■ Operative technique
Preoperative marking was done while the patient in a standing position with a typical Wise pattern skin incision. The Midline was marked from the manubrium sterni to the umbilicus, then marking the mid-axis of each breast from the middle point of the clavicle to the areola. Measuring the distance of the new Nipple Areola Complex (NAC) transposition, the new nippleareola complex position tagged at Pitanguy point.
Dissection of the subcutaneous pocket superior to the new nipple areola complex position, with a distance equal to or more than the required distance of the nipple transposition. The pedicle base was not detached from the posterior region of the pectoralis fascia.
The technique is carried out by First, the areola is marked using the cookie cutter and incised, and depithelialization of the keyhole skin pattern is done using Colorado needle. Then, the breast tissue is excised only caudal to transverse limbs of the pillars down to but not breaching the pectoral fascia. 2 cm-thick pillars are dissected medially, laterally. Superiorly, 0.5 cm-1 cm skin flap is adopted freeing the entire central breast mound. The length of superior/cephalic dissection is equal to the distance needed for NAC superior mobilization. The cephalic pocket must provide an ample room to accommodate the breast tissue to slide with minimal tension.
The constructed central mound is now freely mobile to slide up. Fixation of the central mound upper pole dermis to pectoralis fascia or at the second intercostal space with an absorbable suture 3/0 Monocryl at 9 o’clock, 12 o’clock and 3 o’clock. Finally, meticulous hemostasis, drains were never used.
Once upper pole is fixed, then pillars are wrapped around the central mound and secured using stay stitch to the crossing of the breast meridian with IMF.
Closure is started caudal to cephalic. Initially, closure starts in the horizontal limb from periphery towards centre to enhance the breast perkiness and eliminate dog ears. Usually starting lateral first, done in layers. First layer using barbed suture to block the dead space and prevent the breast falling laterally. Second layer is a dermal layer, followed by the skin layer. Similar way of closure is done medially apart from the first layer “barbed suture layer” which is omitted medially to give more room for the breast to shift medially. Lateral side contour adjustment by liposuction was infrequently used.
Results
A total of 28 patients were included. The mean age was 44.5 years ± 11.2 years, mean body mass index (BMI) 30.2 kg/m2 ± 3.4 kg/m2, 10.7% were diabetic, and all the participants were nonsmokers, as listed in Table 1.
Table 1: Perioperative characteristics.
| Mean age ± SD, year | 44.5 ± 11.2 |
| Mean BMI ± SD, kg/m2 | 30.2 ± 3.4 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 10.7% |
| Mean follow-up ± SD, month | 5.5 ± 0.9 |
| Mean operative time ± SD, minute | 175 ± 9.8 |
| Mean resected breast weight ± SD, gram | 437.3 ± 206.6 |
Preoperatively, 78.6% had Regnault’s grade III ptosis, 14.3% had breast asymmetry, a mean distance from the suprasternal notch to the nipple was 29.4 cm ± 3.9 cm, and nipple to inframammary fold was 12.7 cm ± 2.3 cm.
Mean operative time was 175 minutes ± 9.8 minutes, with resected breast tissue weight being 437.3 gm ± 206.6 gm and mean follow-up period being 5.5 months ± 0.9 months. The following complications were reported: hypertrophic scar n=9 (32.1%), skin flap necrosis n=1 (3.6%), fat necrosis n=4 (14.3%), partial NAC necrosis n=1 (3.6%) and NAC sensation loss n=2 (7.2%). Revision surgery needed in n=5 (17.9%). Most of the patients reported being “Very satisfied” with the results n=27 (96.4%). The postoperative outcomes and complications have been tabulated in Table 2 below.
Table 2: Postoperative outcomes and complications.
| Skin flap necrosis | 3.7% (1) |
| Fat necrosis | 14.8% (4) |
| Partial NAC necrosis | 3.7% (1) |
| Hypertrophic Scar | 33.3% (9) |
| Revision surgery needed | 18.5% (5) |
Discussion
Over the years, many breast techniques were developed and undergone refinement. Many plastic surgeons find it difficult to choose a suitable and reliable pedicle for reduction mammoplasty and mastopexy. Moreover, ongoing arguments still exist regarding the ideal design for a dermo-glandular pedicle, with reliable NAC vascularity and sensation alongside the cosmetic outcomes of shape, size, symmetry, and patient’s satisfaction.
Training and familiarity with the technique are the standards that surgeons base when choosing the surgical procedure. The familiarity with the inferior pedicle approach and the ability to transpose the nipple across long distancesparticularly in large breasts, are reasons why this approach is still used commonly for reduction mammoplasty, despite its associated postoperative issues-such as pseudoptosis (bottoming out) that can develop as early as a few months and progressively get worse [12].
The Central Mound technique generally offers a superior patient’s satisfaction compared with other approaches. This technique can be safely employed in majority of breast types, including gigantic breasts while maintaining satisfactory results and fewer complications. Specific areas where Central Mound excels are the preservation of NAC sensation, NAC viability, and producing an enhanced aesthetic result. Parenchymal circulation is the basis on which nipple-areola viability depends and not on a dermal pedicle [11,13,14].
Overall, postoperatively the breast profile has no concerns throughout follow-up regarding pseudoptosis, recurrence of ptosis and upward rotation of the nipple areola complex. However, these issues and hypertrophic scar tissue occurrence are prevalent when using the inferior pedicle technique [12, 15].
Additionally, the central mound technique gives a well-formed conical shape, upper pole fullness and an aesthetically pleasing projection [3]. This approach can be applied in reductions consisting of any scale and the pedicle length is not an issue-unlike in superior or superiormedial pedicle approach whereby pedicle length is a limiting factor [16,17]. Also, despite several studies concluding that superior or superiormedial reduction in gigantomastia is reliable, there is apprehension about the compromise of the NAC blood supply [9,18-21]. Moreover, other advantages of the central mound approach include eliminating the need for free nippleareolar grafting in large reductions, correction of severe ptosis, and a significant improvement of aesthetic results in more complicated cases such as severe asymmetries [14].
Grant and Ran noted, in their series of 153 patients, a 50% reduction in morbidity rate, a 35% reduction in operating time, no nipple losses, preservation of sensation and vascularity levels were excellent [22]. Also, the CM approach can be carried out in both small and large reductions [23]. When the primary pedicle is unknown, a safer alternative for pedicle design in secondary reduction is a modified central mound. This is attributable to preserving the remaining vascularity in the central mound tissue while simultaneously maintaining the superior and inferior pedicles [24]. Furthermore, the CM technique has proven its reliability and consistency in producing satisfactory results. Thus, it should be considered when dealing with patients undergoing a reduction mammoplasty for macromastia/asymmetry and history of irradiation [25].
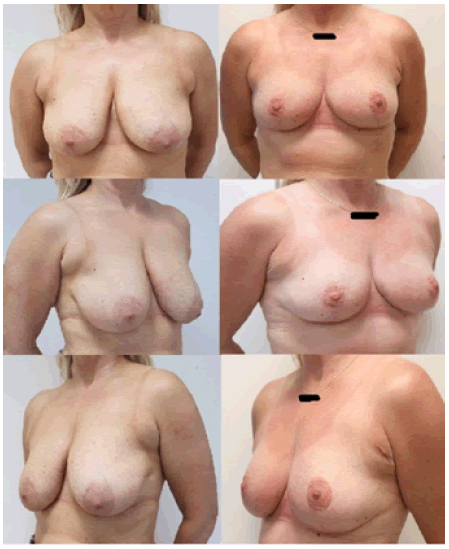
In our retrospective review, we noted that the CM technique had a short operative time because of the limited de-epithelialization. Other positive findings were reduced complication rates, preservation of NAC vascularity and sensation in 92.8%, and 96.4% of patients reported as being “very satisfied” with the result (Figure 1). Regarding complications, the following problems occurred; fat necrosis in 3.5% (n=4), hypertrophic scar in 33.3% (n=9), revision surgery was required in 18.5% (n=5), partial NAC necrosis in 3.7% (n=1), and skin flap necrosis in 3.7% (n=1).
Although our data came from a small sample size, usage of single surgeon technique, limited time to follow up, and subjective postoperative satisfaction, the findings fall in line with and support the currently existing evidence. Further large scale and robust analysis are required to aid understanding, particularly of the relative advantages and disadvantages of the various approaches.
Conclusion
The CM technique has ticked many boxes to justify its prioritization, in ladies seeking reduction mammoplasty. Its versatility, short operative time, perseverance of vascularity and sensation, low complication rates, and pleasing aesthetic result, all affirm its superiority to other techniques.
References
- Foreman KB, Dibble LE, Droge J, et al. The impact of breast reduction surgery on low-back compressive forces and function in individuals with macromastia. Plast Reconstr Surg 124(5), 1393-1399 (2009).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Bilgen F, Ural A, Bekerecioğlu M. Inferior and Central Mound Pedicle Breast Reduction in Gigantomastia: A Safe Alternative?. J Investigat Surg 10, 1-7 (2019).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Kim YS, Hwang K, Kim JH, et al. Central pedicle reduction mammaplasty with a vertical scar: a technical modification. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 51(6), 436-445 (2017).
Google Scholar CrossRef - DeLong MR, Chang I, Farajzadeh M, et al. The Central Mound Pedicle: A Safe and Effective Technique for Reduction Mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 146(4), 725-733 (2020).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Hall-Findlay EJ. A simplified vertical reduction mammaplasty: Shortening the learning curve. Plast Reconstr Surg 104, 748-759 (1999).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Matarasso A. Suction mammaplasty: The use of suction lipectomy alone to reduce large breasts. Clin Plast Surg 29, 433 (2002).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Ramirez OM. Reduction mammaplasty with the “owl” incision and no undermining. Plast Reconstr Surg 109, 512-522 (2002).
Google Scholar - Hidalgo DA, Elliot LF, Palumbo S, et al. Current trends in breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 104, 806-815 (1999).
- Landau AG, Hudson DA. Choosing the superomedial pedicle for reduction mammaplasty in gigantomastia. Plast Reconstr Surg 121, 735-739 (2008).
Google Scholar CrossRef - American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. ASAPS National Data Bank Statistics.
- Balch CR. The central mound technique for reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 67, 305-311 (1981).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Brown RH, Izaddoost S, Bullocks JM. Preventing the “bottoming out” and “star-gazing” phenomena in inferior pedicle breast reduction with an acellular dermal matrix internal brassiere. Aesthet Plast Surg 34(6), 760-767 (2010).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Hester Jr TR, Bostwick J, Miller L, et al. Breast reduction utilizing the maximally vascularized central breast pedicle. Plast Reconstr Surg 76(6), 890-900 (1985).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Hester Jr TR, Cukic J. Central breast pedicle and “free-hand” technique for alteration of volume and skin envelope of the breast. Clin Plast Surg 15(4), 613-625 (1988).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Abramson DL, Pap S, Shifteh S, et al. Improving long-term breast shape with the medial pedicle wise pattern breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(7), 1937-1943 (2005).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Schlenz I, Rigel S, Schemper M, Kuzbari R. Alteration of nipple and areola sensitivity by reduction mammaplasty: A prospective comparison of five techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(3), 743-751 (2005).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Abramo AC. A superior vertical dermal pedicle for the nipple–areola: an alternative for severe breast hypertrophy and ptosis. Aesthet Plast Surg 36(1), 134-139 (2012).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Finger RE, Vasquez B, Drew GS, et al. Superomedial pedicle technique of reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 83(3), 471-480 (1989).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Spear SL, Howard MA. Evolution of the vertical reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstruct Surg 112(3), 855-869 (2003).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Davison SP, Mesbahi AN, Ducic I, et al. The versatility of the superomedial pedicle with various skin reduction patterns. Plast Reconstruct Surg 120(6), 1466-1476 (2007).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Serra MP, Longhi P. The supero-medial dermal-glandular pedicle mastoplasty with Wise pattern: an easy technique with a shorten learning curve is it the gold standard for severe gigantomastia? Ann Ital Chir 81(5), 369-375 (2010).
Google Scholar - Grant III JH, Rand RP. The maximally vascularized central pedicle breast reduction: evolution of a technique. Annals Plast Surg 46(6), 584-589 (2001).
Google Scholar - Hagerty RC, Nowicky DJ. Integration of the central mound technique with the vertical skin takeout reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstruct Surg 102(4), 1182-1187 (1998).
Google Scholar - Spaniol JR, Buchanan PJ, Greco RJ. Secondary reduction mammaplasty: Does initial pedicle design matter? J Plast Surg Hand Surg 53(2), 105-110 (2019).
Google Scholar CrossRef - Weichman KE, Urbinelli L, Disa JJ, et al. Breast reduction in patients with prior breast irradiation: Outcomes using a central mound technique. Plast Reconstruct Surg 135(5), 1276-1282 (2015).
Google Scholar CrossRef